5 ways to build trust in patient data sharing
Posted: May 31, 2023
Primarily, patients entrust their lives and their sensitive personal information to physicians and the entire healthcare ecosystem comprising healthcare providers, insurance providers, specialists, labs, and other third parties at large.
Patient data sharing among various stakeholders for research purposes forms the baseline for innovative new healthcare solutions pertinent to diagnosis, treatments, preventive measures, etc.
Healthcare organizations are increasingly collecting patient data from a variety of sources, such as clinics, wearables, social media, and mobile applications.
While this data can be beneficial for research and marketing efforts, the process raises concerns about the privacy and security of individuals whose sensitive information may be used without their knowledge or permission. This data aggregation practice has the potential to compromise individuals’ privacy, confidentiality, and security.
How do patients feel about their data being shared with third parties
Patients are willing to share their private health information, so long as sharing helps track and manage their health, public health initiatives, or if third parties are directly involved in their treatment. In all cases though, patients prioritize strict privacy and security protocols to be in place to ensure confidentiality of their data. Patients’ trust in an organization’s ethical conduct and purposeful data sharing increases the likelihood of data being shared.
According to a paper in Jama Network Open, the researchers surveyed more than 3,500 individuals in 192 different scenarios about their willingness to share their personal data. Researchers found that individuals were more willing to share their health information if four features of privacy protection were met: consent, transparency of collected data, consumer and regulatory oversight, and the ability to delete data. Consent was the most prioritized feature, followed by data deletion, oversights, and transparency.
Here are five features to build trust in patient data sharing:
1. Consent and transparency
Patient consent and transparency are essential in forming a trusting relationship between patient and provider. Consent allows patients to be in control of their data, meaning they are able to make informed decisions about their healthcare and can revoke or restrict information sharing whenever they want. To ensure trustworthiness within an organization, policies should emphasize open communication that explains the type of data sharing, who will have access to the data, and the potential risks or benefits.
What should healthcare organizations do?
- A transparent privacy policy should be the cornerstone of all communication, including providing clear and concise information about their data collection, use, sharing, and safeguarding practices
- Implement a robust consent and preference management system that offers granular consent management options and provides mechanisms to easily revoke or modify consent preferences.
2. Data privacy and security
Today’s healthcare environment has seen an influx of data breaches and security incidents, creating a heightened awareness among patients surrounding the potential risks of mishandling personal data. This has made it increasingly important for healthcare organizations to demonstrate their commitment to protecting patient data by taking comprehensive privacy and security measures.
What organizations should do?
- Instill a sense of confidence in consumers that their data is being handled carefully, with protective measures in place such as encryption, access controls, and DSAR requests
- Demonstrate commitment to consumer privacy and minimize the risks associated with excessive data sharing or storage by collecting only the necessary amount of data and processing it for specific, well-defined purposes
- Continuously monitor data protection practices and mitigate potential security risks by conducting regular vulnerability assessments and security audits and training employees on data privacy and security awareness.
3. Compliance with regulations
The data privacy landscape is consistently evolving in order to ensure greater protection for individuals. Health data protection laws such as HIPAA have been instrumental in safeguarding the private health information of patients; however, advancements in technology, such as wearables, mobile applications and social media platforms, have necessitated the implementation of new regulations. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) ensures data privacy and security across Europe, while the Washington State’s My Health, My Data Act has been implemented to protect health data collected from wearables, apps and other digital sources.
What organizations should do?
- Be compliant with all the applicable laws and regulations that apply to different types of health data as per their sensitivity
- Monitor and stay updated on the evolving regulatory landscape
- Take a proactive stance when implementing and enforcing policies, procedures, and technical measures that guarantee the organization meets all applicable compliance requirements.
4. Data sharing and agreement
The exchange of health-related data plays a key role in enabling healthcare, with data being shared between various entities to provide healthcare providers with comprehensive patient information, support medical research, and identify any potentially concerning public health trends or patterns.
This type of data sharing can bring immense benefit to the healthcare industry; however, it must be conducted in accordance with agreements that protect against the risks of unauthorized access, data breaches, privacy concerns, compliance violations and loss of data ownership. To ensure this level of security, organizations need to implement comprehensive policies and procedures related to health data.
What should healthcare entities do?
- Data sharing agreements should provide comprehensive data protection and security measures for users’ data. These measures should ensure that users’ personal information is stored securely, is inaccessible to unauthorized persons, and is used only for the purposes stated in the agreement
- Agreements should outline the roles, responsibilities, and legal obligations of the parties involved in data sharing to ensure compliance with relevant regulations
- Agreements should address issues such as data ownership and data usage limitations as part of the legal and contractual framework for sharing data.
5. Education and patient empowerment
Many patients may not, at first, fully understand the complexities of consent management or the implications of data sharing. However, they will be willing to share data if made aware of the benefits, risks, and choices associated with sharing their health data.
What should healthcare institutions do?
- Investing in educational initiatives is key to ensuring individuals can truly understand the implications of health data sharing. To do this, resources, such as FAQs, informational videos and privacy guides, should be made readily available.
- Involve patients in the design and governance of health data sharing initiatives to foster a sense of ownership and trust.
- Seek patient input through surveys, focus groups, or patient advisory boards to comprehend their concerns, suggestions, preferences, etc.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations should consider patients’ concerns regarding their health data being shared with third parties. With the current reluctance to share this kind of information, numerous opportunities in the healthcare sector will be missed. In order to overcome this barrier, healthcare organizations must find ways to boost consumer confidence in data sharing by revising their policies and introducing features that will alleviate these privacy concerns.
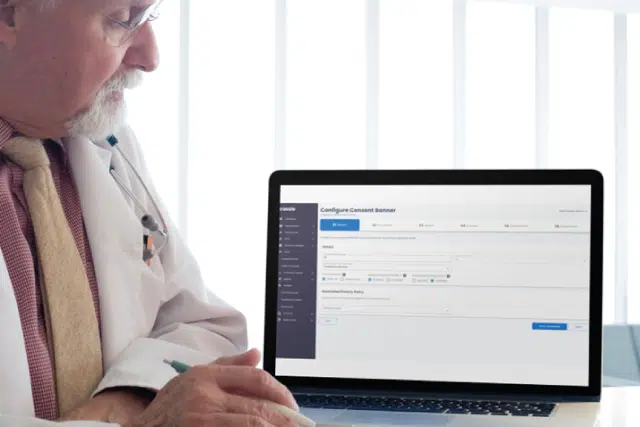
Cassie helps healthcare providers build patient trust
- Cassie’s fully compliant Consent and Preference Management platform gives patients control over their information, so they can see what is being collected and who has access to it
- Cassie helps keep patient data safe and secure, following the rules of HIPAA. This way, healthcare providers can make sure that patient data is used correctly and only with the permission of the patient
- Cassie also provides an audit trail for any changes and access permissions, giving healthcare providers added peace of mind that their patient data is secure.
By using Cassie, healthcare organizations can provide patients with increased trust in sharing their personal information. This will help to ensure that both parties have a better understanding of how the data is used and helps to create long-lasting relationships between healthcare organizations and their patients.
Cassie gives healthcare providers the opportunity to focus on building patient trust and achieve the following goals:
- Ensure full HIPAA and GDPR compliance (and any other regulation that affects them)
- Ensure that patients’ personal data is securely stored
- Provide a complete audit trail of all access permissions and changes
- Provide a convenient way to track, manage, and share sensitive data securely
- Better understand how patient data is being used and ensure that it is used appropriately

Want to know how Consent Management Platforms can help healthcare providers achieve HIPAA compliance quickly?
Discover how HIPAA has revolutionized the healthcare sector, uncover its three biggest flaws and find out what happens when rules are broken, with our HIPAA compliance: expectations vs. reality guide.