Legislation
HIPAA compliance: Protect health data
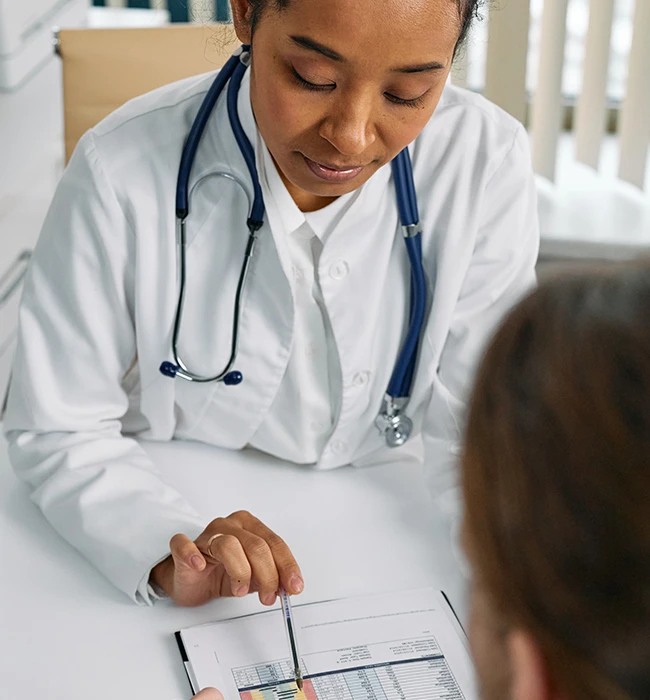
Meet HIPAA compliance requirements with Cassie: a comprehensive consent management platform that secures sensitive PHI, enables granular patient control and protects patient privacy.


The primary goal of HIPAA is to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ health information. It includes provisions that set national standards for the electronic exchange of health information and addresses the confidentiality and security of healthcare data.
Key components of HIPAA include:
Privacy rule: This rule establishes national standards for the protection of individually identifiable health information. It gives patients control over their health information and sets limits on who can access and use it.
Security rule: The Security Rule specifies a series of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information (ePHI).
Breach notification tule: This rule requires covered entities and their business associates to notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media of breaches of unsecured PHI.
How Cassie CMP can help you achieve HIPAA compliance
Protect patient privacy
Empower patients with granular consent controls to ensure patient confidentiality and strengthen trust, with enforcement across domains, devices and platforms
Ensure data security
Cassie is SOC 2 certified, assuring healthcare organization’s sensitive patient data and PHI are safeguarded from unauthorized access or breaches with industry-leading encryption protocols and practices
Avoid severe penalties
Cassie is designed to help organizations meet the complex requirements of HIPAA and mitigate risk with a robust framework for managing consent, avoiding severe penalties and reputational damage
Demonstrate HIPAA compliance
Automated compliance tracking provides audit trails to demonstrate compliance alongside advanced RoPA and DSAR modules to improve efficiencies and assess risk
Centralized source of truth
Use Cassie to honor and enforce consent data across all downstream platforms (CRMs, EHRs, patient portals) at high volume, in real-time for HIPAA compliance across your ecosystem
Complex consent made simple
For every consent captured, Cassie can store unlimited key value pairs of additional information against those consents to unlock scalable, granular consent management
Platform features
Further HIPAA guidance
HIPAA FAQs
-
What does HIPAA mean?
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a 1996 US federal law that sets the national standards to protect sensitive patient health information (PHI) from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge.
-
Who needs to comply with HIPAA?
-
- Covered entities (anyone providing treatment, payment, and operations in healthcare), for example: medical practitioners, hospitals, clinics, health plan providers, healthcare clearinghouses
- Business associates (anyone who has access to patient information and provides support in treatment, payment, or operations), for example: billing companies, EHR vendors, IT service providers, consultants and auditors
- Subcontractors and any other related business associates must also be in compliance with HIPAA
-
-
What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
- The HIPAA Privacy Rule establishes national standards for protecting individuals’ medical records and other personal health information. It requires that covered entities implement safeguards to protect patient privacy by limiting unnecessary access to PHI as well as requiring established policies around how to use and disclose PHI in specific scenarios like public disease control or personal treatment purposes.
-
What is the HIPAA Security Rule?
-
The HIPAA Security Rule focuses on protecting electronic personal health information (ePHI) specifically, setting guidelines for technical safeguards with an organization’s IT infrastructure. There are three main categories of the Security Rule:
- Administrative safeguards to ePHI protection, like risk assessments, training programmes and response plans
- Physical Safeguards to secure physical access to where ePHI is stored, like facility access controls, workplace security measures and device disposal policies
- Technical Safeguards to secure technological solutions that access ePHI, like encryption tools and firewalls
-
The HIPAA Security Rule focuses on protecting electronic personal health information (ePHI) specifically, setting guidelines for technical safeguards with an organization’s IT infrastructure. There are three main categories of the Security Rule:
-
What is a violation of HIPAA?
- Common violations include unauthorized access to PHI without authorization, failure to notify individuals or authorities of data breaches within the timeframe, and inadequate training that leads to negligence or lack of physical, technical or administrative safeguards of ePHI.