GDPR compliance vs CCPA compliance
Posted: June 10, 2021
GDPR compliance vs CCPA compliance – what is the difference?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of laws implemented in the European Union to protect citizens’ personal data within the EU. It applies to any company or organization that processes, stores or uses the personal data of any individual within an EU member state. The GDPR provides clear guidelines on what companies must do to ensure their systems and processes comply with GDPR regulations.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a law created by the state of California that has gone into effect as of January 1st, 2020. The law aims to give Californians stronger control over how businesses use their data and requires companies to disclose certain information when consumers ask. Like GDPR, CCPA applies to businesses that collect, store or use an individual’s personal data within California.
The General Data Protection Regulation and California Consumer Privacy Act share the common goal of protecting consumers’ privacy.
GDPR and CCPA are designed to give individuals greater control over their personal data and impose significant restrictions on how companies can collect, use, store and disclose customer information.
However, there are some key differences between these two regulations which organizations should be aware of when it comes to compliance:
- One of the major differences is in terms of enforcement. The GDPR is enforced by European data protection authorities in all 28 EU countries, but each member state has slightly different interpretations based upon local laws. On the other hand, enforcement for the CCPA lies with the Attorney General of California.
- Another difference is that the GDPR applies to any organization, regardless of size and location, involved in collecting or handling data from EU citizens. The CCPA only applies to organizations with more than $25 million in annual revenue or which handle personal information from 50,000 or more consumers per year.
- The breadth of what data falls under the scope of each regulation is also different. The GDPR includes both personal and sensitive data such as political opinions or religious beliefs, whereas the CCPA does not cover sensitive information like race, religion, sexual orientation etc.
- Finally, while both have provisions for customers to access their data and ask companies to delete it (right to be forgotten), opt-out of data sales, and receive an explanation when their data has been used in automated decision-making, these are handled differently under each regulation. Under the GDPR, companies are required to provide customers with information about how their data is being used upon request and must delete it if requested within 30 days, while the CCPA does not have a specific timeline for providing such information or deleting data.
In summary, organizations should be aware that there are differences between GDPR and CCPA regarding compliance. It’s important to understand each regulation separately and ensure your organization complies with all relevant regulations to protect consumer privacy.
GDPR vs CCPA the comparison
Only in the GDPR:
- Restrictions on how and why businesses can process personal data
- Additional protections for Sensitive Personal Data
- Privacy by design and privacy by default requirements
- Opt-in consent as a legal basis of processing
Only in the CCPA:
- Personal information includes data about devices and households
- Right to Object/Opt-Out only covers the sale of personal information (narrower than GDPR Right to Object)
- Access rights are broader
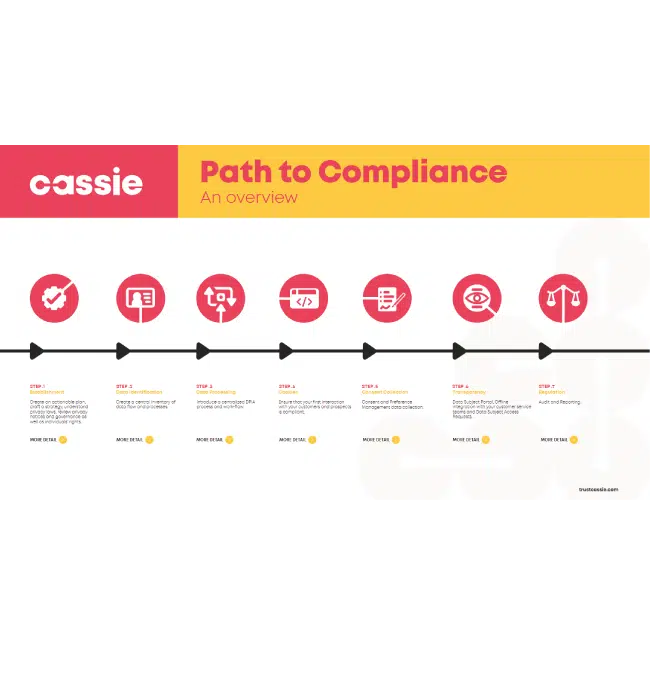
Want to learn more about global data privacy compliance
If you’d like to learn more about how we can help you on your compliance journey, read our path to compliance guide.